Structure and function of cell and its organelles, Intercellular connections
Structural and functional unit of living body
Structure of the Cell
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm & its Organelles
- Nucleus
- Outer covering, protective sheath, plasma membrane, plasmalemma
- Semipermeable membrane, free exchange of certain substances between ECF and ICF
Composition
- Proteins (55%) – Lipids (40%)
- Carbohydrates (5%)
Structure
- Fluid mosaic model
- 1972, SJ Singer and GL Nicholson
- Membrane is a fluid lipid bilayer with mosaic of proteins
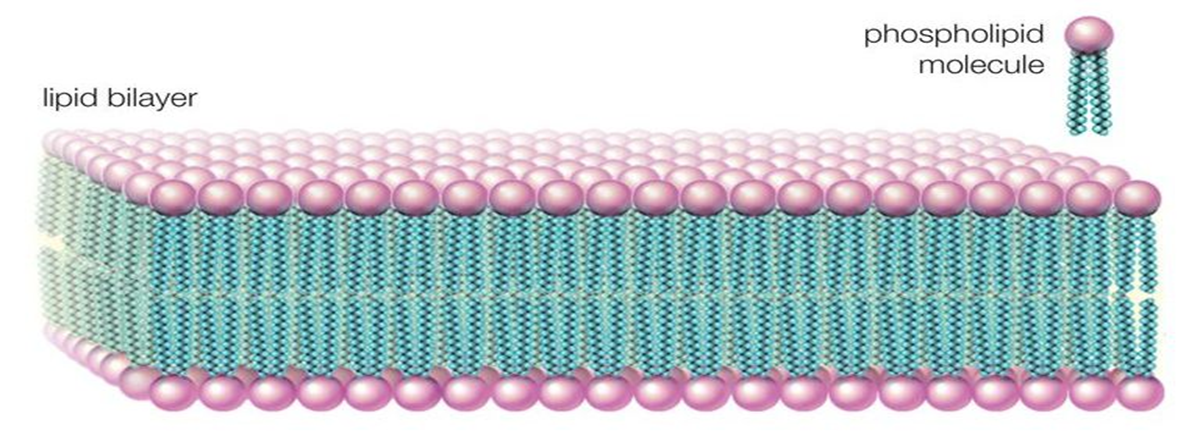
Lipid bilayer
- Phospholipids
- Cholesterol
Phospholipids
- Phosphorus (Head)
- Fatty acid chain (Tail)
Proteins in the Cell membrane
- Integral or transmembrane proteins
- Peripheral or peripheral membrane proteins
Integral or Transmembrane protein
- Pass through entire thickness of cell membrane
- Tightly bound to the cell membrane
Eg:
- Cell adhesion proteins
- Cell junction proteins
- Some carrier (transport) proteins
- Channel proteins
- Some hormone receptors
- Antigens
- Some enzymes
Peripheral proteins
- Partially embedded in the outer and inner surfaces of the cell membrane and do not penetrate
- Loosely bound with integral proteins or lipid layer – easily dissociate
Eg:
- Proteins of cytoskeleton
- Some carrier (transport) proteins
- Some enzymes
Functions of Proteins in Cell Membrane
- Integral proteins - Structural integrity
- Channel proteins (Water channels)
- Carrier or transport proteins
- Pump (Na-K ATPase)
- Receptor proteins (Hormones, NTs)
- Enzymes
- Antigens
- Cell adhesion molecules
Carbohydrates on Cell Membrane
- Proteoglycons
- Form a thin and loose covering over the entire surface of the cell membrane – Glycocalyx
Functions
- Repel negative charge ions
- Cell adhesions
- Receptors (Hormones)
Overall functions of Cell Membrane
- Protective function
- Selective permeability
- Absorptive function
- Excretory function
- Exchange of gases
- Maintenance of shape and size of the cell
Cytoplasm
- Jellylike material, 80% water
- Organelles
Membrane junctions
Connection or contact between neighbouring cells or the cell and extracellular matrix
Classified into 3 types 1. Occluding junctions
Communicating junctions 3. Anchoring junctions
Occluding Junctions
Prevent intercellular exchange of substances (movement of ions and molecules from one cell to another)
Eg: Tight Junctions (zonula occludens)
Apical margins of epithelial and endothelial cells in intestinal mucosa
Wall of renal tubule
Capillary wall and choroid plexus
Structure
Made of ridges from both cells
Ridges - tight junction strands & proteins • Proteins
Tight junction membrane proteins
Eg: Occludin, Claudin and Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs)
Scaffold (framework or platform) proteins / Peripheral membrane proteins / Cytoplasmic plaque proteins
Eg: Cingulin, Symplekin And ZO1, 2, 3.
Functions
Strength and stability
Selective permeability (gate function)
Fencing function (prevents the lateral movement of proteins)
Maintenance of cell polarity – Blood-brain barrier
Dysfunction
Applied Aspects
Hereditary deafness – Ichthyosis
Sclerosing cholangitis
Hereditary hypomagnesemia – Synovial sarcoma
Communicating Junctions
permit the intercellular exchange of substances (allows passage of ions and smaller molecules between the cells)
Eg: Gap Junction (Nexus) – Heart
Basal part of epithelial cells of intestinal mucosa
Structure
Adjacent cells lie very close
Cytoplasm of the two cells is connected by the channels
Molecules move from one cell to another cell without contact with ECF
Channels – proteins - connexins or connexons
Functions
Permits passage of glucose, amino acids, ions and other substances
Helps in exchange of chemical messengers between the cells
Helps in rapid propagation of action potential from one cell to another
Dysfunction
Applied Aspects – Deafness
Keratoderma – Cataract
Peripheral neuropathy
CharcotMarieTooth disease – Heterotaxia
Anchoring Junctions
provide strength to the cells by acting like mechanical attachments
Structural integrity (severe mechanical stress) – Heart muscle
Epidermis of skin
Firm attachment due to – Actin filament
Intermediate filament
Classification
Actin filament attachment
Adherens junction (cell to cell) 2. Focal adhesion (cell to matrix)
Intermediate filament attachment 1. Desmosome (cell to cell)
Hemidesmosome (cell to matrix)
Adherens Junction
Connects actin filaments of one cell to those of another (cell to cell)
Zonula adherens
Membranes held together by transmembrane proteins called cadherins
Helps withstand severe mechanical stress • Intercalated disks of cardiac muscle
Epidermis of skin
Focal Adhesion
connects actin filaments of the cell to extracellular matrix (cell to matrix)
Membranes held together by transmembrane proteins called integrins
Structural integrity
Desmosome
Cell to cell junction
Intermediate filaments – Macula adherens
Transmembrane proteins - cadherins
Hemidesmosome
Cell to matrix junction – Intermediate filaments – Macula adherens
Transmembrane proteins – integrins
Applied Physiology
Dysfunction of adherens junction and focal junction in colon – Colon cancer
Dysfunction of desmosomes and hemidesmosomes causes bullous pemphigoid (autoimmune disease with tense blistering eruptions of the skin)
Antibodies development against cadherins and integrinsCell Adhesion Molecules
Cadherins
Adherens junction and desomosome • Integrins
Focal adhesion and hemidesmosome • Igg super family
Nervous system • Selectins
Platelets and endothelial cells